Improving bus stops will make public transportation safer and more enjoyable. In early 2022, Long Beach Transit (LBT) was looking for solutions to its challenges in maintaining the condition of bus stops and bus stop amenities. It provides bus transportation in Los Angeles and Orange County. The company has a fleet of 250 buses across 14 cities covering 100 square miles. The company has a ridership of more than 23 million customers.
It uses Geographic Information System (GIS) technology to generate interactive and static route network maps and analyze ridership patterns across its service area. The GIS supports the transit business by enabling staff to plan, maintain, and locate transit infrastructure. GIS analysts regularly fulfill map and data requests and keep the GIS databases and web maps current as the bus timetables and routes are updated. Check out more here: GIS Data Catalog.
Timeline
The project team was a coalition of three companies, Long Beach Transit (LBT), Environmental Research Institute (Esri), and Quartic Solutions. LBT uses Esri’s ArcGIS platform for their GIS and thus turned to Esri for guidance in choosing an ArcGIS-based solution. ArcGIS Field Maps, along with a customizable survey template, were selected. Quartic Solutions, a woman-owned Esri business partner and premier GIS services firm was chosen to provide GIS staffing and expertise to LBT in March 2022.
Early 2022
The project started.
June 2022
A prototype was successfully tested.
Summer 2023
The first stage of systemwide fieldwork will begin in the summer 2023.
The Challenge
Public transportation in Los Angeles is essential to many people’s everyday lives. Long Beach Transit ensures everyone feels safe and can enjoy the entire bus experience, from waiting for the bus to reaching their final destination.
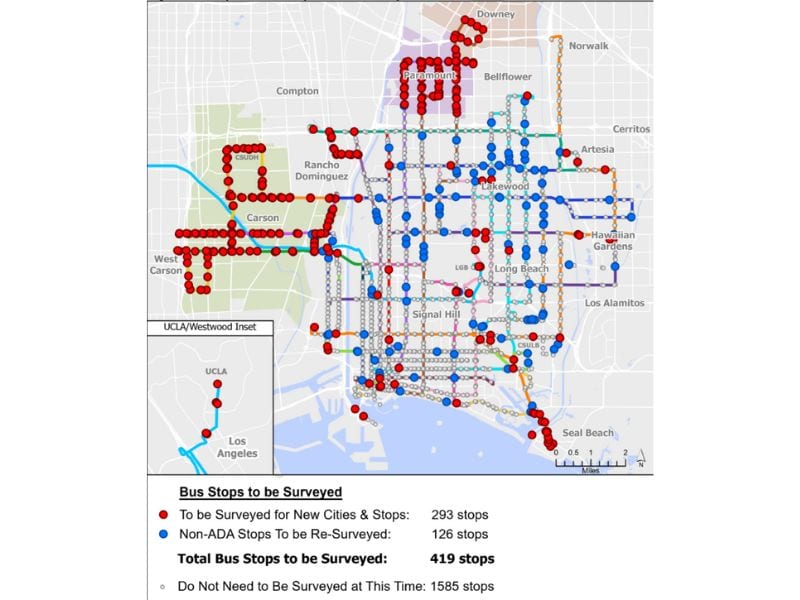
LBT (Long Beach Transit) has over 2,000 bus stops in its service area. While their Transit Customer Amenities (TCA) Department is responsible for maintaining the cleanliness at each bus stop, they have faced some challenges. Issues like how to maintain an up-to-date database of site conditions, ensuring ADA accessibility, and making sure amenities are maintained and available at each bus stop. The condition information about the bus stops is critical and necessary for making sound decisions, such as which bus stops need improvements. TCA had a legacy solution that provided access to the bus stop data but was looking for additional tools to help make its employees’ jobs easier.
In 2012, LBT developed a bus stop survey containing basic information about bus stops. After using the old system for over ten years, the staff knew exactly what they wanted to change. They needed a solution that would help minimize data entry errors during the field data collection and provide a new option for capturing photos. Being able to attach photos would really help staff record details of the visual conditions at specific locations.
They also wanted a more streamlined, user-friendly application interface. By standardizing the wording of the amenity inventory, they felt they could reduce data entry errors, such as typos and non-accurate descriptions. The plan was to develop a database better suited for storing complex infrastructure relationships (1 to many relationships). Then, design an application allowing supervisors to review and approve work. Adding better data tracking associated with bus stop amenities was also important.
Cloud-Based GIS Solution
The three organizations worked well together to address and resolve the complications LBT was facing with their previous legacy software. The project team architected a cloud-based solution using AWS infrastructure and the Esri ArcGIS platform. The solution included a mobile field map data collection application and an on-premise web mapping application.
A solid foundation for the project was built by cleaning and loading existing data into a new database. The data were organized into 14 related tables covering a wide variety of information such as passenger amenity types, amenity conditions, comments, and pictures. Then, crucial data regarding ADA compliance was incorporated. The traffic condition data was added to enrich the dataset, including the site conditions, such as the stop area location and pedestrian crosswalks.

The field data collection application was created using the survey template included with ArcGIS Field Maps. The Field Maps App is available for download via the Apple App Store and/or Google Play Store. Once downloaded, the Field Maps App was configured for LBT staff, and tools to minimize user input errors, archive data, and facilitate editing were included.
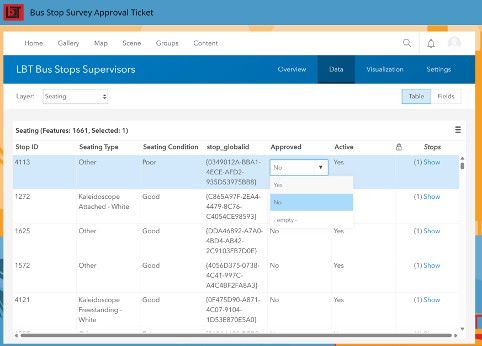
Offline data collection is built into the Field Maps App. Once a field user is reconnected to the network, the local data stored in the Field App is uploaded to the ArcGIS Portal. Then, after the sync, a supervisor can view the approval screen, where all the new and/or edited records are presented in an intuitive table format, ready to approve.
The Service Planning Bus Stop Web Application offers more advanced functionality when staff is on-premise. The Bus Stop Web App is a web map containing current LBT stops, active routes, and historical ridership data combined with the new bus stop amenity data. The color of the bus stops easily visualizes the staff’s progress in the field. Staff can quickly review a stop’s amenity data in pop-up menus by clicking on the map.
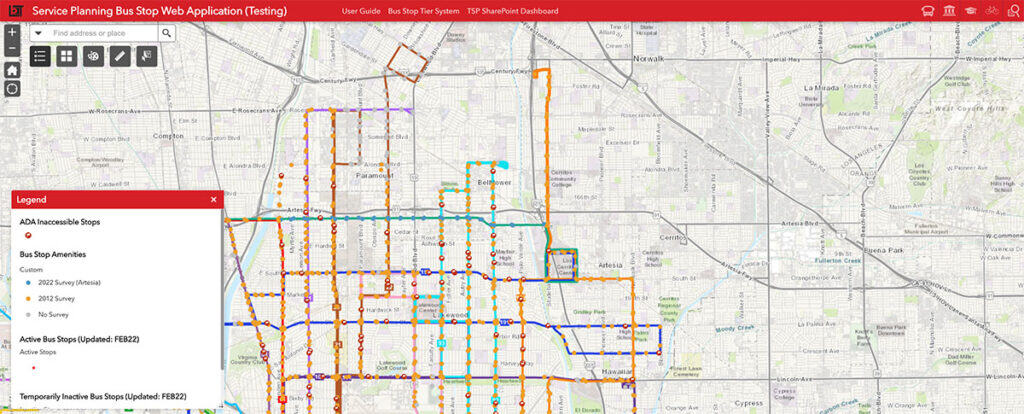
LBT makes service changes to its service network three times a year. To facilitate these recurring service changes, the solution also includes functionality to automatically add new stops and inactivate old stops if a new service change is initiated.
Clean Bus Stops, Clean Data
Like in every complex project, there were some obstacles to overcome. In this case, the challenge arose when incorporating the old 2012 amenity data. The data was collected as one big database table with no relationship classes. Specific amenities had multiple values and duplicate entries. To load the old data to the new normalized tables, Quartic designed an ETL model that appended and split data as needed for the improved schema. Data cleanup tasks, such as standardizing to coded domain values, were automated, resulting in a tidy dataset with increased data integrity.
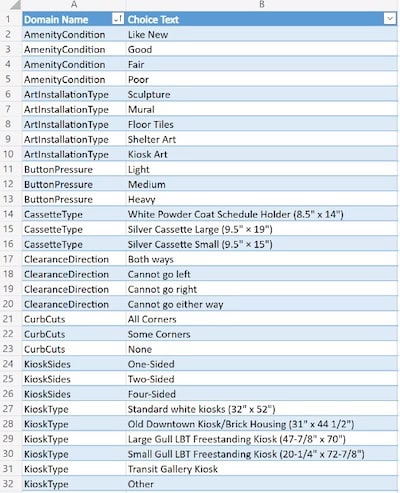
Picture 5. is a screenshot of an example of the coded value domains – the left column is the domain name to be assigned to certain fields, and the right is the options for that domain. This prevents users from making spelling/formatting errors.
Successful Journey
With the data being collected and turned into an easy-to-read format, LBT can provide up-to-date bus stop amenities and ADA information to the public and transit customers. LBT staff can more easily identify which bus stops have accessibility improvements and the condition of those improvements. They can collaborate with related government agencies, such as municipal public works departments, to better prioritize crosswalk and sidewalk pedestrian improvements. The restructured data and new application architecture were tested in June 2022 by LBT staff by collecting bus stop amenities and ADA information. The test used the Metro Route 130 service transition to LBT Route 141. The first stage of systemwide fieldwork will begin in the summer of 2023.
Based on the successful conclusion of the prototype project, LBT will consider planning a larger 0system-wide implementation and rollout, incorporating the updated bus stop data into LBT’s GIS databases alongside the GTFS (General Transit Feed System) network, land use, ridership, and demographic information. This is an example of how GIS technology can support transit operations and make public transit safer and more enjoyable.
“Quartic has extensive experience with a highly qualified GIS technical service team.” – Service Development Manager, Long Beach Transit

